Klystrons
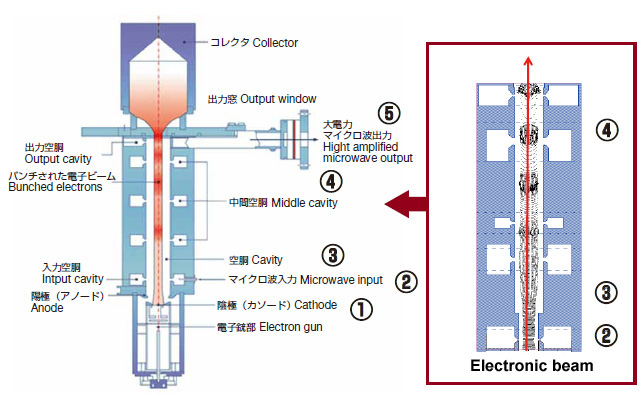
Structure & Principle of operation
- Electrons emitted from the cathode are accelerated by the anode and enter the input cavity.
- The electrons may be accelerated (positive phase) or decelerated (negative phase) depending on the phase of the microwave input from the input cavity. (This is known as velocity modulation.)
- Accelerated and decelerated electrons become grouped (density modulation) while passing through a uniform electric field in the interaction section, and gradually become bunched.
- The bunched electrons are gradually enlarged by self-induced microwave fields in the middle cavity section.
- Finally, as the bunched electron beam passes through the output cavity, it induces a strong alternating electric field, which is output through the output window as an amplified microwave.
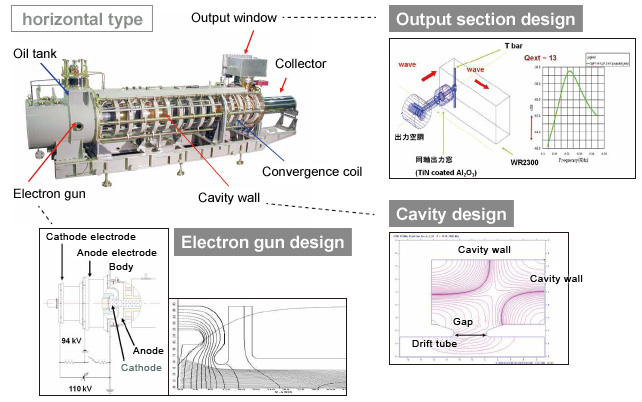
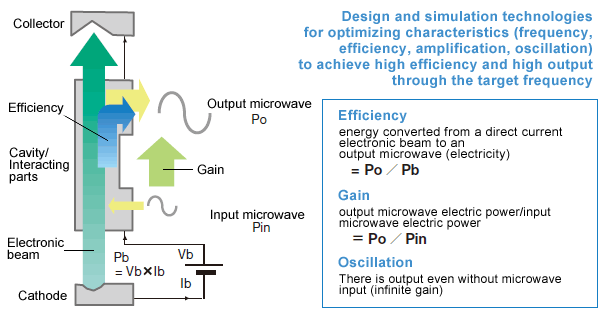
Core Technology
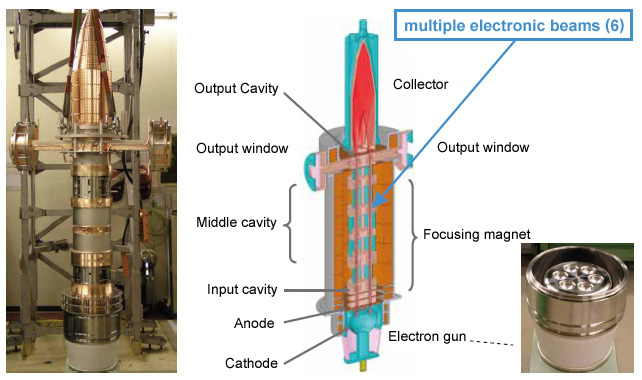
Multi-beam efficiency
- Enhance η efficiency by lowering perveance K
- Overall beam current is increased through multiple beams. Also accommodates low-voltage driving.
Multi-beam elemental technology
Complex design simulation technology is required to combine multiple electronic beam characteristics.
- Electromagnetic field simulation
- Thermal analysis simulation
- Structural analysis simulation
New type : horizontal Multi-Beam Klystron (MBK) for Euro-XFEL


